What does a future Uniandino Environmental Engineer study?
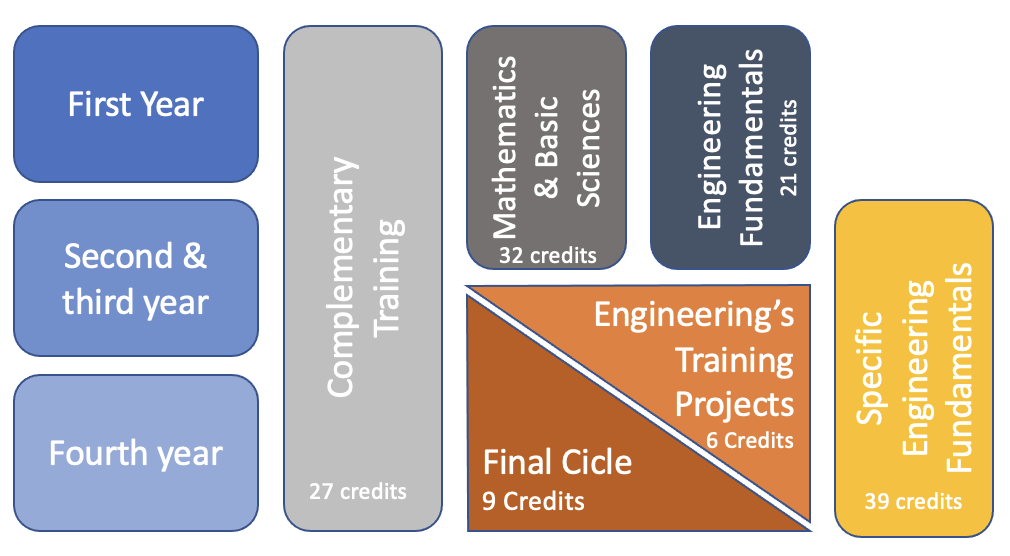
Our study plan in Environmental Engineering has the following knowledge areas:
- Mathematics and Basic Sciences: Includes foundation courses in science and mathematics, such as calculus, physics, and chemistry.
- Engineering Fundamentals: Includes foundation courses in science and mathematics, such as calculus, physics, and chemistry.
- Specific Engineering Fundamentals: These include the specific courses of the program, which lay the foundations for the formal exercise of the profession in each of the areas of Civil Engineering.
- Engineering's Training Projects: They include the courses final project of design and project of degree.
- Final Cycle: Consisting of deepening elective courses.
- General Education: Cycle transversal to all the programs of the Universidad de los Andes, including comprehensive training courses and courses in citizenship.
In the specific training in Environmental Engineering, you will have the possibility to choose the area in which you want to deepen, among the following options:
- Characterization, modeling, analysis and control of air pollution: it is focused on understanding the causes and phenomena that determine the generation, emission, concentration and distribution in the air of different pollutants and odors; how air pollutants are distributed at urban and rural levels; and what are the levels of exposure of the population to these pollutants.
- Public, occupational and environmental health: studies the relationship between environmental pollution and health problems in the population.
- Characterization, modeling, analysis and sustainability of hydrosystems and ecosystems: Develops technical monitoring protocols and laboratory analysis methods for the characterization of conventional and emerging determinants of water quality, bioindicators and toxic substances present in hydrosystems and ecosystems, in addition to the development of tools and methods of analysis and mathematical modeling of transport processes, reaction kinetics and biochemical transformations of said determinants and pollutants, in order to promote the rational and sustainable use of water resources and ecosystems.
- Hydrology, meteorology and climatic variability: It focuses on the characterization, quantification, analysis, modeling, development of tools and knowledge of hydrological and meteorological processes, including their variability associated with changes in land use, and climatic variability related to macroclimatic phenomena. and climate change, within a context of hydrosystems and ecosystems, in order to promote the rational and sustainable use of water resources.
- Management and sustainable management of solid, hazardous waste and contaminated sites: One of the fundamental objectives of this line is the generation and dissemination of knowledge that supports the development of public policies and environmental regulations aimed at the management and sustainable management of solid waste and dangerous.
- Sustainable management of supply systems and wastewater and rainwater:
- Environmental chemistry, biotechnology and nanotechnology: studies the chemistry of the environment focused on the development of technologies for the control and prevention of pollution, as well as the use of living systems (macro and microorganisms) for the development of products of environmental interest.
Tipo de elemento:
Enlace
Orden:
5